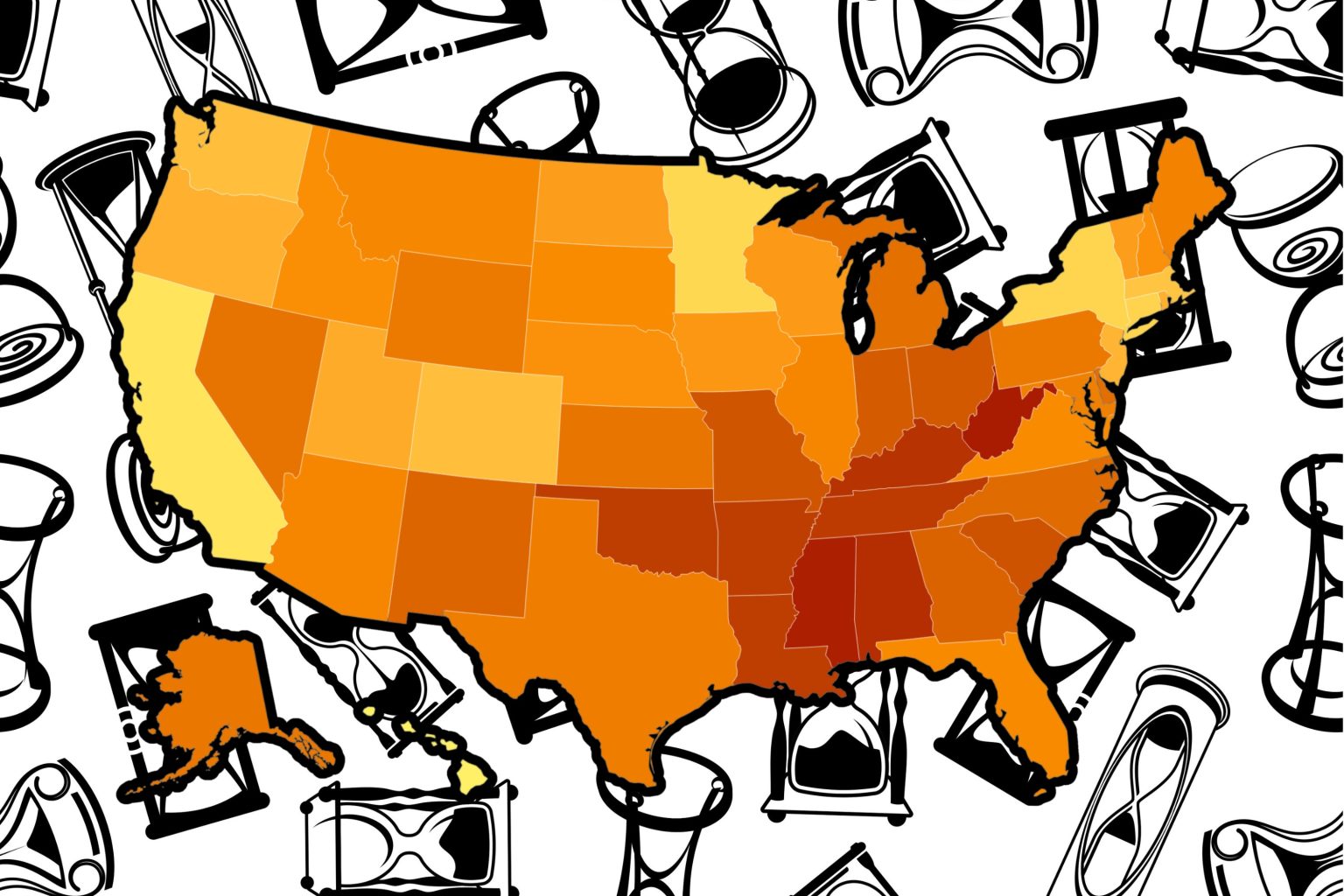
A recent study by Jessica Ho, an associate professor of sociology and demography at Penn State, revealed that America has the lowest life expectancy among all English-speaking countries. The research compared life expectancy data from the Human Mortality Database and World Health Organization Mortality Database from 1990 to 2018 for the United States, Canada, Ireland, the United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand. The findings indicated not only a low overall life expectancy for the U.S. compared to other countries but also significant geographical variations within the nation. There are stark disparities between regions, with parts of the West and Northeast performing better while the South and Appalachia lag behind.
One potential reason for the disparities in life expectancy across the U.S. could be the divergence in urban and rural life expectancies since the 1990s. Large central cities and their suburbs have seen significant gains in life expectancy, while smaller cities and nonmetropolitan areas have experienced lower life expectancy levels with minimal improvements. Factors contributing to these disparities include differences in health behaviors such as smoking, sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, illicit drug use, and alcohol abuse. Selective migration patterns, where healthier individuals move to cities and coastal states, leaving behind less healthy populations, as well as variations in access to healthcare and distance to hospitals, may also play a role.
Specific states in the U.S. have been identified as having the lowest life expectancies in 2018, including West Virginia, Mississippi, Alabama, Kentucky, and Tennessee. Conversely, Hawaii, California, Minnesota, New York, and Connecticut were among the states with the highest life expectancies for that same year. In order to address these disparities and improve America’s overall life expectancy, a focus on reducing avoidable deaths among younger citizens is crucial. This includes implementing policies that improve access to treatment for drug addiction and overdose, reducing road traffic fatalities, investing in public transportation, decreasing gun deaths, and combating cardiovascular disease.
The study underscores the need for targeted interventions to address the inequalities in life expectancy across different regions of the U.S. To raise life expectancy and improve overall population health, efforts must be made to target specific risk factors and health behaviors that contribute to premature mortality. By addressing issues such as drug addiction, road traffic fatalities, gun-related deaths, and cardiovascular disease, significant improvements in life expectancy can be achieved. Collaborative efforts involving policymakers, healthcare providers, community organizations, and individuals are essential to reducing disparities and promoting better health outcomes for all Americans.