On 1 May 2004, the European Union saw its largest enlargement in history, known as the “Big Bang”, with ten new countries joining the bloc. These countries were Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Hungary, Malta, Poland, Slovakia, and Slovenia, increasing the number of member states from 15 to 25. This move expanded the EU’s population by almost 75 million people overnight, making it one of the world’s largest single markets. The integration of these new countries has led to significant economic growth, with countries like Poland and Malta seeing their economies more than double since joining the EU.
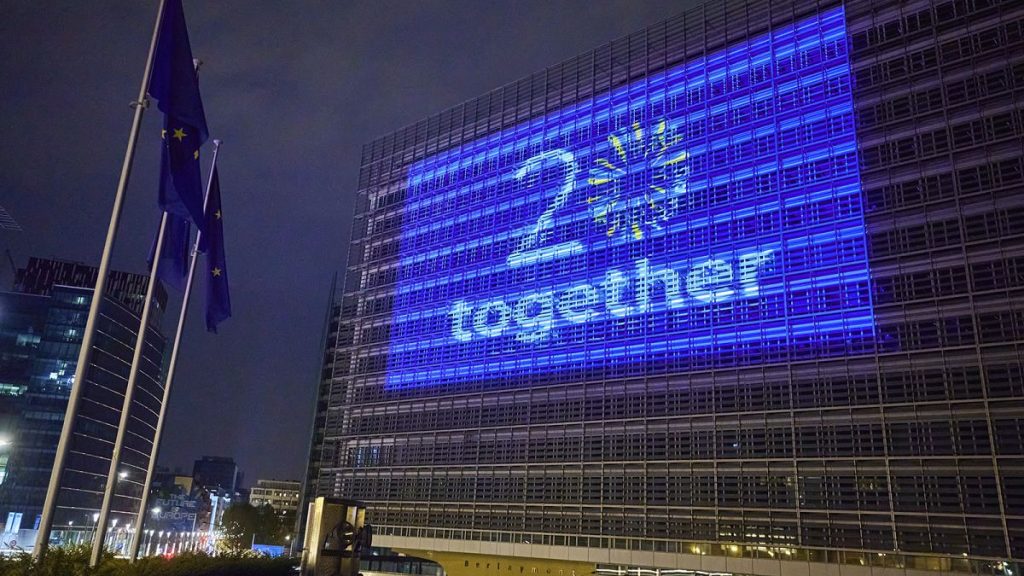
The EU marked the 20th anniversary of this historic enlargement with a colourful celebration, with buildings such as the European Commission, the European Parliament, and the EU building in Luxembourg lit up in blue and yellow, projecting the slogan “20 Years Together”. The expansion in 2004 has had a positive impact on job creation in the EU, with around 26 million new jobs emerging since the enlargement. A significant portion of these jobs, six million, were created in the ten countries that joined the EU in 2004. Additionally, the expansion allowed 2.7 million young people to participate in the Erasmus+ programme, promoting education and cultural exchange within the EU.
Economic data from the EU shows that countries that joined the EU in 2004 have experienced substantial economic growth since their integration. For example, the economies of Poland and Malta more than doubled, while Slovakia saw an 80% growth in its economy. The increase in job opportunities and economic growth has had a positive impact on the overall prosperity of these countries. The EU’s expansion has also strengthened its position as a global economic player, creating one of the largest single markets in the world with a diverse range of member states and populations.
The EU’s enlargement in 2004 has not only boosted economic growth and job creation but has also contributed to the overall prosperity and stability of the European Union. The addition of ten new countries from eastern Europe has enriched the diversity of the EU and has created opportunities for increased cooperation and exchange among member states. The integration of these countries has allowed for closer ties and shared values among EU countries, promoting unity and solidarity within the bloc. The EU’s expansion has also enhanced its position as a leading global player, with a strong economic presence and influence on the international stage.
The 2004 enlargement of the EU has had significant long-term benefits for both the new member states and the existing member states. The access to a larger single market has provided new opportunities for trade and investment, contributing to economic growth and prosperity across the entire EU. The integration of the eastern European countries has also led to increased cultural exchange and cooperation within the EU, fostering a sense of solidarity and unity among member states. The EU’s expansion has paved the way for further growth and development within the bloc, creating a stronger and more cohesive European Union that is better equipped to face the challenges of the future.
The EU’s enlargement in 2004 marked a significant milestone in the history of the European Union, with ten new countries joining the bloc and contributing to its economic growth and prosperity. The integration of these countries has led to increased job creation, economic growth, and cultural exchange within the EU, strengthening its position as a prominent global player. The expansion has also promoted unity and cooperation among member states, fostering a sense of solidarity and shared values within the EU. The benefits of the 2004 enlargement continue to be felt across the EU, with increased opportunities for trade, investment, and collaboration contributing to the overall prosperity and stability of the European Union.