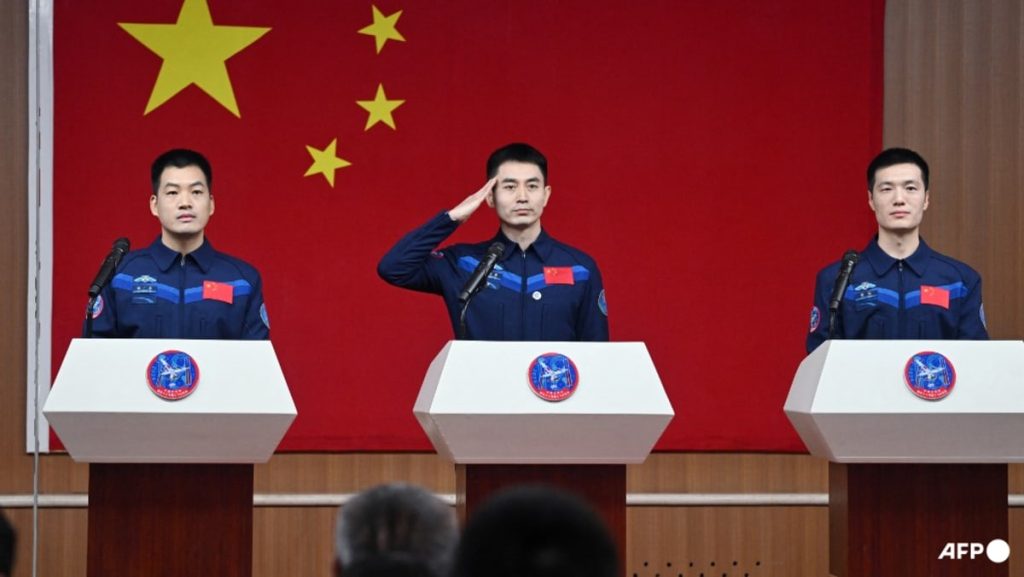
ke off from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in northwest China, with the crew expected to spend six months on board the space station. This will be the second crewed mission to the Tiangong space station following the successful launch of the Shenzhou-12 mission last year. The mission marks another significant step in China’s ambitious space exploration goals.
The Tiangong space station, which translates to “Heavenly Palace”, is a key component of China’s space program and is expected to be fully operational by 2022. The station is designed to be a platform for scientific research, technology demonstrations, and international cooperation in space exploration. The successful completion of the Shenzhou-18 mission will bring China closer to establishing a permanent human presence in space.
China has been making rapid progress in its space program in recent years, with successful missions to the Moon, Mars, and now the Tiangong space station. The country’s long-term goal is to send astronauts to the Moon by 2030, a feat that has so far only been achieved by the United States. China’s ambitious space exploration plans have raised concerns in some quarters, with some experts warning of the potential militarization of space.
Despite these concerns, China’s space program has been met with admiration and respect from the international community. The country has made significant strides in developing its own space technology, including its own rocket engines, spacecraft, and space station. China has also been active in international collaborations, such as the Tiangong-1 space lab project with the European Space Agency.
The launch of the Shenzhou-18 mission will be closely watched by space enthusiasts around the world, as China continues to demonstrate its capabilities in space exploration. The successful completion of the mission will bring China one step closer to its goal of establishing a permanent human presence in space. The crewed mission to the Tiangong space station is expected to further boost China’s reputation as a prominent player in the global space community.
The upcoming Shenzhou-18 mission represents a significant milestone for China’s space program, as the country continues to make strides in its ambition to send astronauts to the Moon by 2030. The mission will not only contribute to scientific research and technology demonstrations but also enhance China’s capabilities in space exploration. As China’s space program continues to evolve, it is likely that the country will increasingly play a key role in shaping the future of space exploration.